
Profound and Detailed
2024-08-28
As an important component for the radiation and reception of wireless signals, antennas play a key role in wireless communications. How exactly does the antenna convert the signal from wired to wireless? What are the key parameters of an antenna, and how to evaluate the performance of an antenna? This series of articles will give you an in-depth understanding.
An antenna is a device used to transmit or receive radio waves. It converts electrical energy into electromagnetic energy and then radiates it to free space, or converts electromagnetic energy in free space into electrical energy.
According to the characteristics of the horizontal pattern:
There are many types of antennas. According to the characteristics of the horizontal pattern, antennas can be divided into omnidirectional antennas, directional antennas and smart antennas.
 Omnidirectional antenna:
Omnidirectional antenna:
• The radio wave energy radiated by an omnidirectional antenna is the same in all directions in the horizontal plane, but the radio wave energy radiated in different directions in the vertical plane is different.
• Pattern radiation is similar to the visible light radiated by an incandescent lamp, radiating 360 degrees in the horizontal direction.
 Directional antenna:
Directional antenna:
• Directional antennas radiate different radio energy in all directions in the horizontal and vertical planes.
• Pattern radiation is similar to the visible light radiated by a flashlight. It radiates in a certain direction. With the same radio frequency energy, a longer coverage distance can be achieved, but at the expense of the area it covers.
 Smart antenna:
Smart antenna:
• Smart antennas have multiple directional radiation and 1 omnidirectional radiation pattern in the horizontal plane.
• The antenna receives the signal transmitted by the terminal in omnidirectional mode; the smart antenna algorithm determines the location of the terminal based on the received signal, and controls the CPU to send control signals to select the directional radiation mode with the maximum radiation direction pointing towards the terminal.
In the direction of polarization
According to the polarization direction, it can be divided into single polarization antenna and dual polarization antenna.
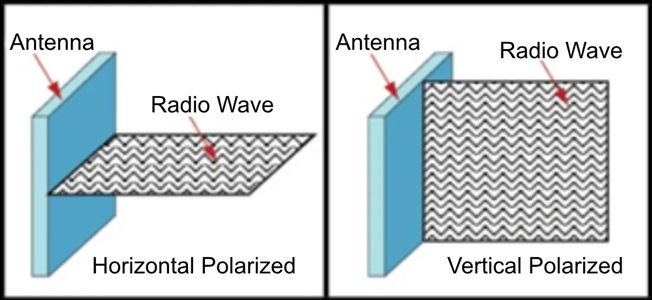
Single polarized antenna:
• It consists of a conductor, simple structure and has only one polarity. When transmitting and receiving signals, a single-polarized antenna usually requires two antennas, one responsible for signal transmission in the horizontal direction and the other responsible for the vertical direction.
• Single-polarized antennas can achieve omnidirectional radiation, that is, they can radiate or receive electromagnetic waves uniformly in different directions.
• Single polarized antennas usually have broad frequency band characteristics and are suitable for different communication systems and frequency bands.
• Although single-polarized antennas are relatively simple in structure, they have unique advantages in applications that require omnidirectional radiation or broadband characteristics.
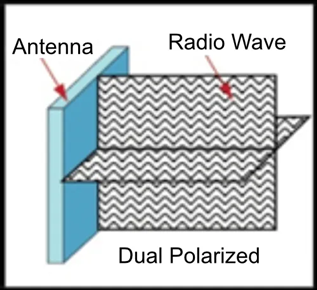
Dual polarized antenna:
• It combines two antennas with polarization directions of +45° and -45° that are orthogonal to each other, and works in transmit and receive duplex mode at the same time. This design allows dual-polarized antennas to independently transmit and receive information in both horizontal and vertical directions.
• Dual-polarized antennas can independently transmit and receive signals in horizontal and vertical directions, enhancing the system's flexibility and strong signal reliability.
• Dual polarized antennas are widely used in wireless communication systems due to their advantages in saving space, providing system flexibility and signal reliability, especially in space-constrained environments.
By material or structure
Divided by material or structure, common ones include PCB antennas (board-mounted antennas), ceramic antennas, rod antennas, suction cup antennas, etc.
• PCB antenna (board-mounted antenna) has the advantages of small size, light weight, low cost, easy installation and debugging, and is very suitable for small and portable devices. Microcyber's A1110 wireless adapter uses a PCB antenna.
• Ceramic antennas have the advantages of long signal transmission distance, high flexibility, and resistance to electromagnetic interference. They are usually used in wireless networks, security monitoring and other applications.

• Rod antennas are large and need to be installed outside the user product casing. Microcyber’s NCS-TT105W wireless temperature transmitter and G1100 wireless gateway both use rod antennas.
• The suction cup antenna has a long lead and can be installed at a certain distance from the user's product, but its performance is affected by the object it is attracted to.

Microcyber WirelessHART Series Products
Microcyber's smart wireless products use WirelessHART wireless technology that focuses on process automation. It has the characteristics of self-organizing network, self-healing, low power consumption, data encryption, etc., ensuring reliable operation and flexible and fast installation. Through our wireless modules, wireless gateways, wireless adapters, wireless temperature transmitters and other products, we can quickly realize data collection, process monitoring, equipment operation, maintenance and diagnosis of complex industrial sites. Microcyber's smart wireless products have become the preferred industrial wireless communication solution for domestic end customers. Internationally renowned companies have also joined the ranks of cooperation, and have been widely used in petrochemical, electric power, metallurgy, machinery manufacturing and other fields.
<< Previous page
Next page >>