
Profound and Detailed
Introduction to Wireless Industrial Communication Technology
2024-07-16
Industrial wireless has huge development potential
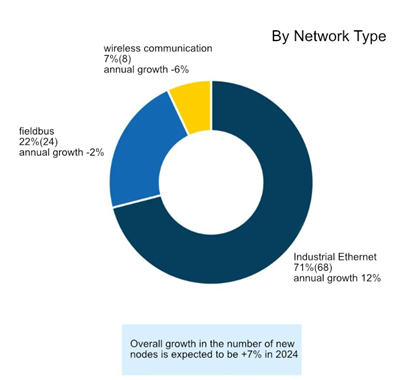
Latest research from HSM Networks shows that the industrial networking market continues to expand, with growth expected to grow 7% in 2024. It's worth noting that wireless technology has grown steadily in recent years, although the rate of growth has slowed slightly according to reports. By network type, wireless solutions still account for 7% of the total share. The market continues to introduce more industrial wireless-enabled products, and the acceptance of wireless solutions in factory environments is growing. Typical use cases include cable replacement applications, wireless machine access and connectivity to mobile industrial equipment.
 Germany's "Industry 4.0 R&D White Paper" and "Industry 4.0 Implementation Strategy and Reference Architecture" both regard wireless technology as an important component of Industry 4.0 network communication technology research and innovation.
Germany's "Industry 4.0 R&D White Paper" and "Industry 4.0 Implementation Strategy and Reference Architecture" both regard wireless technology as an important component of Industry 4.0 network communication technology research and innovation.
 The American Industrial Internet Consortium IIC attaches great importance to the application of wireless technology in industry. The alliance has specially established a network connection group to carry out research on network technology.
The American Industrial Internet Consortium IIC attaches great importance to the application of wireless technology in industry. The alliance has specially established a network connection group to carry out research on network technology.
The reason why German Industry 4.0 and the American Industrial Internet attach great importance to the application of wireless technology in industry is because wireless networks have obvious advantages over existing industrial wired networks.
● Significantly reduce network construction and maintenance costs. Wireless networks can be deployed quickly, and cables and related protection devices can be laid wirelessly on sites, workshops, factories and other environments. Installation and maintenance costs are reduced.
● Improve the flexibility of the production line. Wireless technology enables the mobility of field equipment and enables flexible and rapid reconstruction of production lines based on industrial production and application needs.
● Achieve a wide range of deployment environments. Because wireless technology breaks through the limitations of cable deployment and has various network architectures such as mesh and star, it can achieve rapid deployment in a variety of industrial scenarios.
Wireless technologies involved in industrial networks
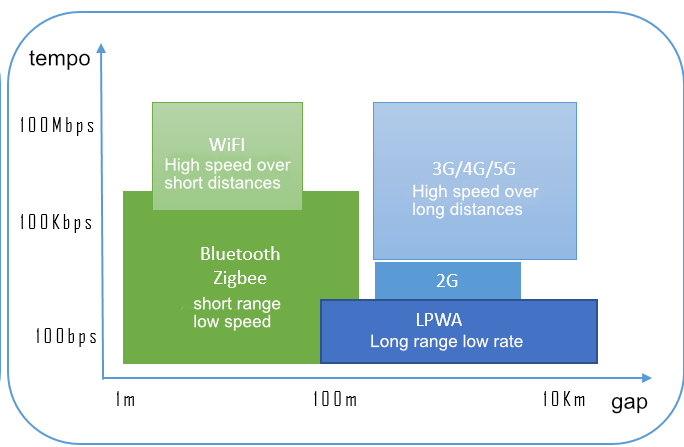
According to the wireless communication distance, wireless communication technology can be divided into short-range wireless communication technology and wide-area network communication technology:
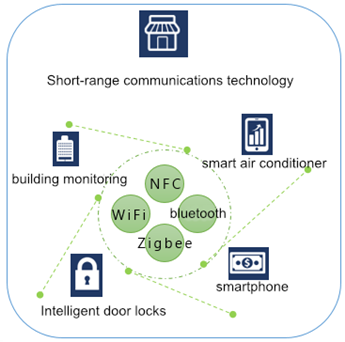
● Short-distance wireless communication technology: including traditional short-distance communication technologies such as WLAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee and RFID, and dedicated short-distance communication technologies for industrial applications represented by WirelessHART, ISA100.11a, WIA-PA, etc.
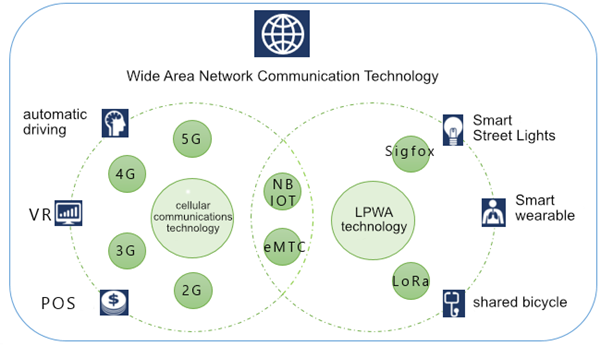
● Wide area network communication technology: including 2G/3G/4G/5G cellular technology and LPWA technology, NB-IOT and eMTC are licensed spectrum technologies, and LoRa and SigFox are unlicensed spectrum technologies.
Wireless technology features
The application of wireless networks in industry requires different levels of optimization design based on its application links and the services it carries. According to the wireless communication speed, wireless communication can also be divided into high-speed communication and low-speed communication. Typical wireless technology application scenarios are shown in the table.
Category | Communication Distance | Communication Rate | Typical Application |
Bluetooth | 10m | 20M | Short-distance communication,audio streaming, file synchronization |
WiFi | 50m | 200M | Home or office network,online videos, large games and file downloads,etc. |
Zigbee
| 200m | 250kbps | 2.4G frequency band,low speed and low power consumption. Used for IoT devices, such as sensor data communication and home appliance remote control. |
WirelessHART | 200m | 250kbps
| 2.4G frequency band,low speed,low power consumption and high reliability. A lot of technical optimization has been done for industrial sites in terms of reliability, anti-interference and delay guarantee. |
LoRa
| 1-20km
| 0.3-5kbps
| SubG free licensed frequency band,smart agriculture,smart buildings, logistics tracking,need to build your own network. |
NB-IoT
| 1-20km
| <250kbps
| SubG authorized frequency band,water meter,parking,pet tracking, smoke alarm,using operator network. |
5G
| 500m
| 1Gbps
| High speed,low latency,large number of connections,high reliability, autonomous driving,drones,VR/AR,smart factories and smart medical care. |
The development trend of wireless networks will be mainly superposition and supplemented by integration
Industrial control systems are self-contained and take stability and reliability as the first criterion, so industrial companies are very cautious about their modifications. Enterprises such as industrial manufacturing and industrial services have an urgent need for data on production equipment, environment, production tools, etc. In addition, wired deployment is too expensive and difficult, so they have adopted an overlay method to deploy wireless networks.
The overlay method refers to building a wireless network outside the existing factory network to collect equipment and product information, and perform non-real-time and real-time equipment control in some scenarios. Some companies are also trying to adopt a converged approach to deploy wireless networks, that is, using wireless networks to gradually replace some of the existing industrial control network terminals (such as field buses and large networks) to achieve wireless information collection and control.
<< Previous page
Next page >>